Angioplasty and Stent Placement for Heart:
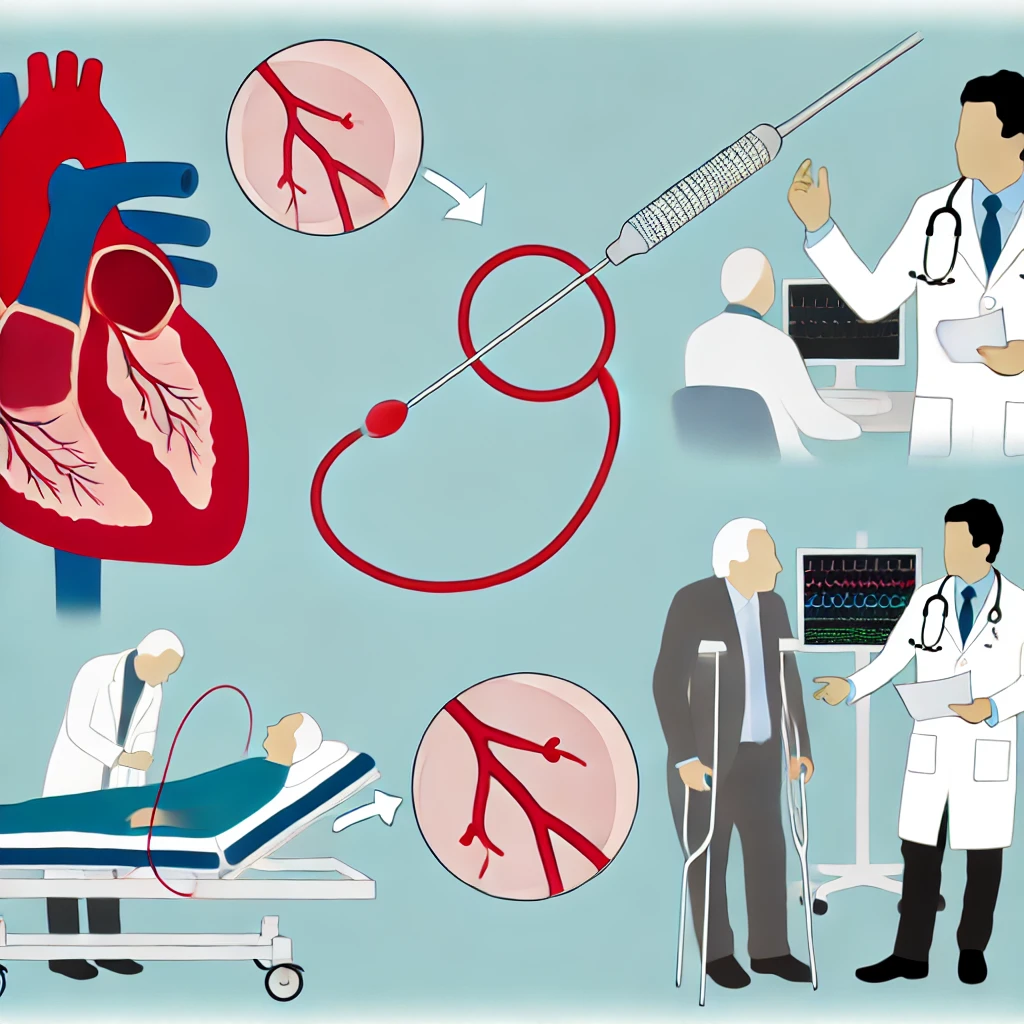
Throughout the world, the heart disease is one of the main reasons why people die. That is why, angioplasty and stent placement are highly effective and common ways to cure this illness. These procedures are employed for unclogging blocked arteries in the heart, hence enhancing circulation of blood and reduction of risks of heart attacks.
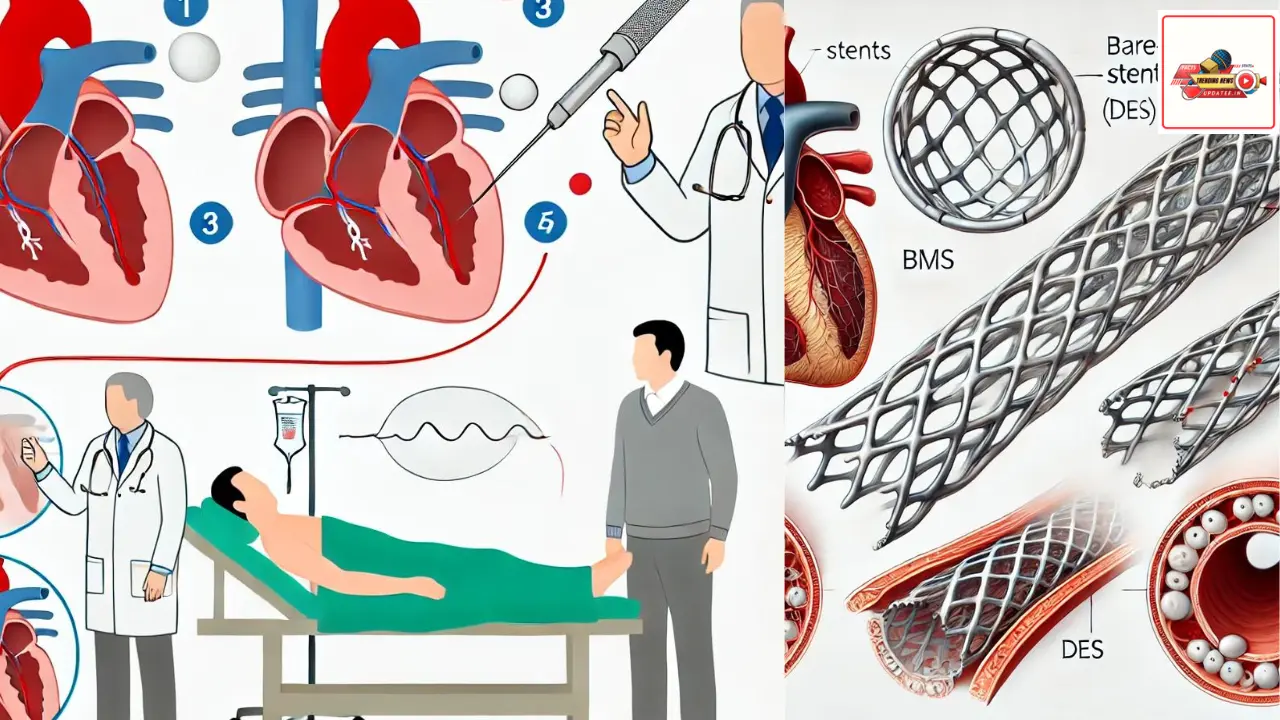
Coronary stents are now often used in almost all angioplasty procedures after a heart attack. A stent is a small machine that looks like a mesh coil. It is inserted into the artery and opened. The artery can be prevented from shrinking or closing again.
After successful stent placement, tissue begins to form on the stent like a layer of skin. The stent will be completely filled with tissue within 3 to 12 months. The period of time depends on whether the stent has a drug coating or not.
 Coronary Stents
Coronary Stents
You may be given medicines called antiplatelets to reduce the stickiness of platelets. Platelets are special blood cells that stick together to stop bleeding. Medication can also prevent blood clots from forming inside the stent. Your healthcare team will give you specific instructions about which medicines to take and for how long after stent placement.
 Types of Stents
Types of Stents
Bare-Metal Stents (BMS): These are uncoated metal stents that help keep the artery open by acting as supports.
Drug-Eluting Stents (DES): These stents are coated with medication that is slowly released to prevent the artery from becoming blocked again. This medication aids in decreasing the probability of restenosis (re-narrowing of the blood vessels).
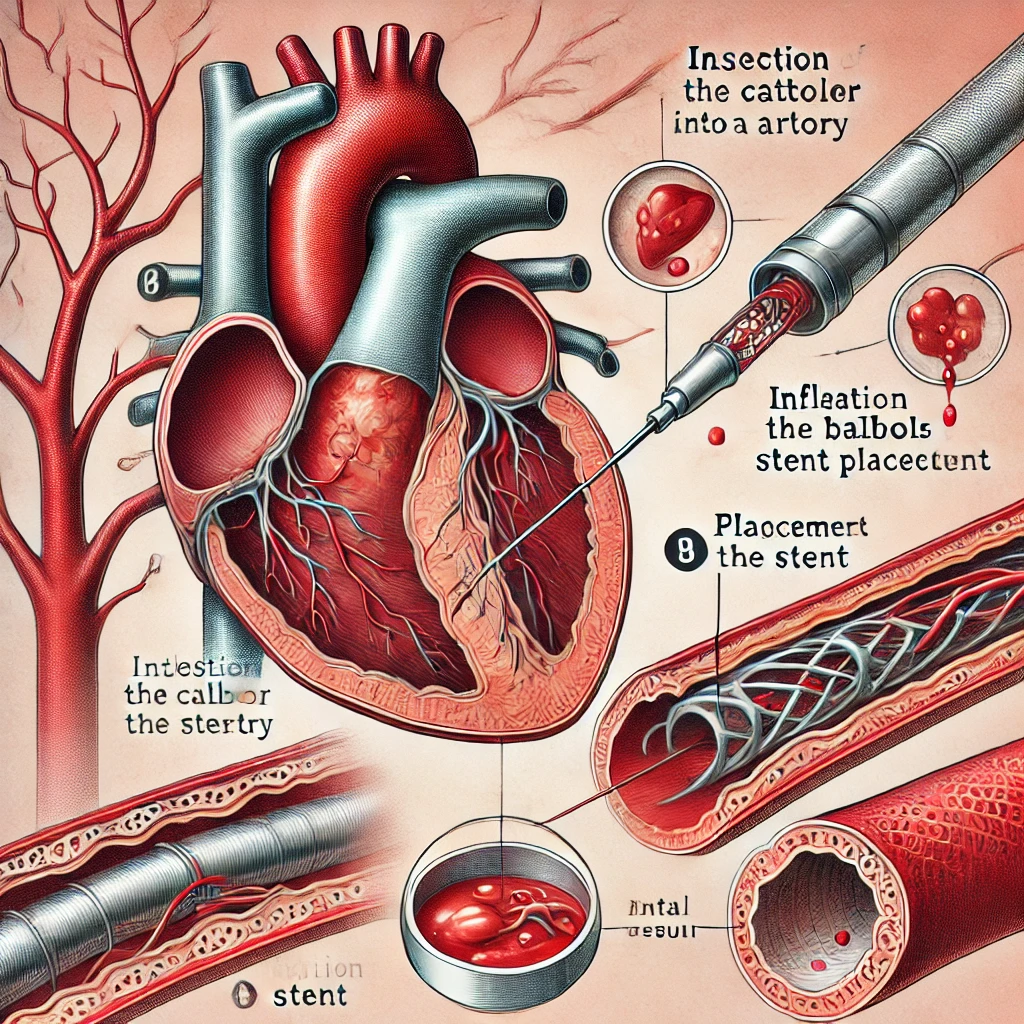 How does a stent work?
How does a stent work?
Most stents are coated with medication to prevent scar cells from forming inside the stent. These stents are called drug-eluting stents. They release medication into the blood circulation that slows down the overgrowth of cells inside the stent. This helps prevent the blood circulation from narrowing again.
Some stents do not have this drug coating and are called bare metal stents. They may have a higher rate of stenosis. But they do not require long-term use of antiplatelet medicines. This may be the preferred stent for people who are at high risk of bleeding. The stent works by correcting these. If you have chest pain after having a stent put in, you should talk to your healthcare team.
 What are the risks of angioplasty?
What are the risks of angioplasty?
Potential risks associated with angioplasty, stenting, atherectomy, and related procedures include:
- Bleeding problems occur at the site where the catheter is inserted into the body (usually the groin, wrist or arm)
- a blood clot or damage to the blood circulation from the catheter
- Blood clot in the blood circulation
- Infection at the catheter insertion site
- heart disease
- heart attack
- Stroke
- chest pain or discomfort
- Rupture of a coronary artery or complete blockage of a coronary artery. Which requires open-heart surgery.
- allergic reaction to the contrast dye
- kidney damage from the contrast dye
 Angioplasty and stent placement are highly significant operations that allow patients with coronary artery disease to live longer or in a better way. Although this surgical treatment may have some dangers, it is essential to the modern therapy in cardiology, due to its role in reestablishing blood circulation preventing heart attacks.
Angioplasty and stent placement are highly significant operations that allow patients with coronary artery disease to live longer or in a better way. Although this surgical treatment may have some dangers, it is essential to the modern therapy in cardiology, due to its role in reestablishing blood circulation preventing heart attacks. Disclaimer: Some of the information given in the news is based on media reports. Before implementing any suggestion, please consult the concerned expert.