
Brain Health:
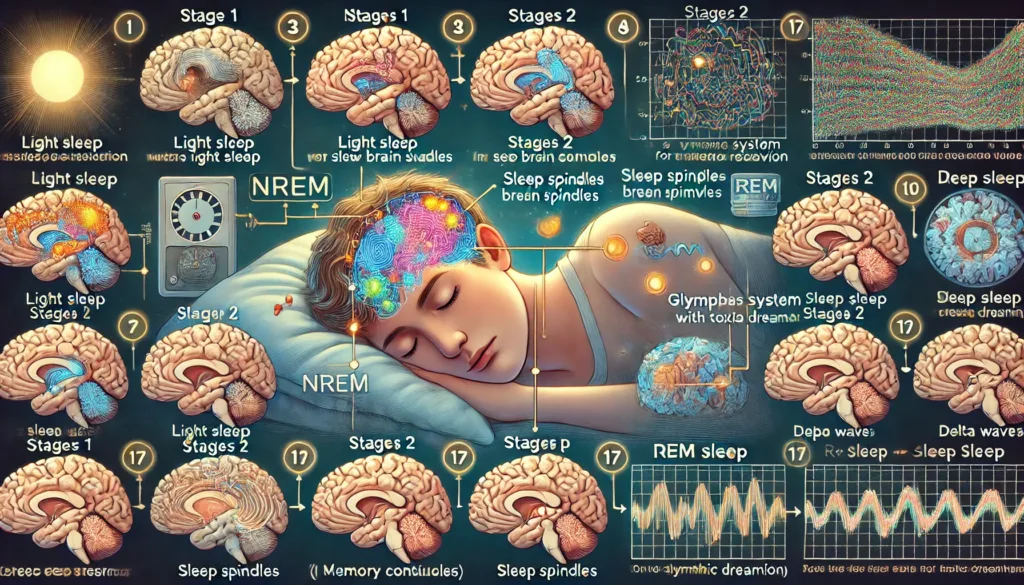
Every year, on 22nd July, we celebrate World Brain Day to celebrate brain health in order to remind people how important it is to maintain your mental health. Let’s explore what happens to the brain health as we sleep by delving deeper into the (complex and mysterious,) process of sleep in which this beautiful, yet complex (in its ability to influence our mental state…) organ plays a crucial part.
The Stages of Sleep:
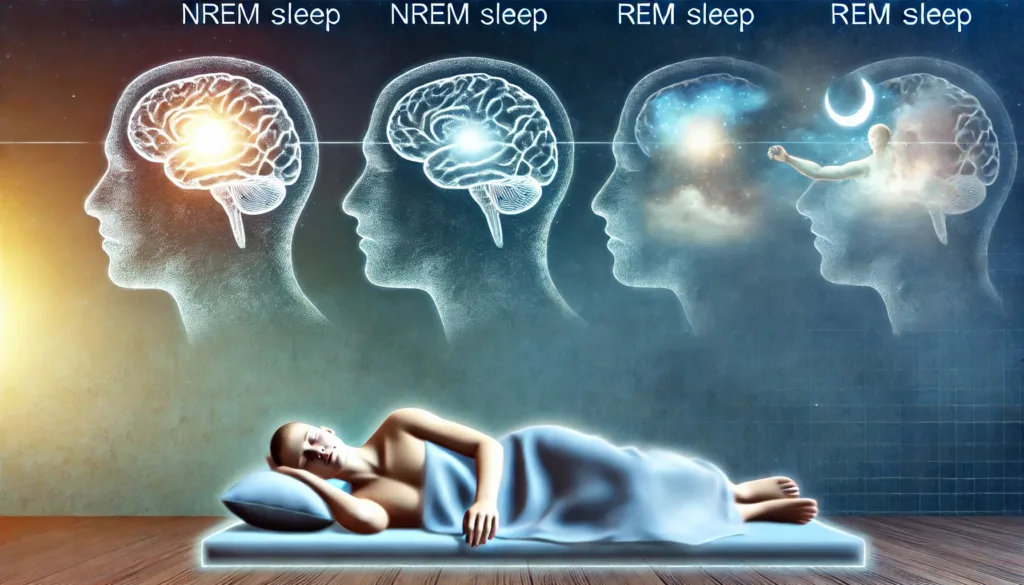
There are two principle types of sleep and one of them is characterized by the Non rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep while the other is characterized by rapid eye movement (REM) sleep just like in the human condition. It should be known that sleep does not exist as a single uniform state; it is instead constantly changing and made up of numerous stages that change throughout the period of time when it occurs.
NREM Sleep:
NREM Sleep is divided into three main stages:
Stage 1: This is the first stage in NREM sleep cycle with light sleep and occasional drifting into wakefulness. The period is dominated by the production of high amplitude theta brain waves that are slow. There is fall in muscle tone and slow eye movement under the closed eyelids.
Stage 2: Here eye movements cease and there are slower brain waves plus short spurts of rapid-wave spindle activity. When we hit stage two our body temperature falls due to a decreased heart rate.
Stage 3: This stage is characteristic by the production of delts brainwaves which are slowest frequency range with highest intensity on an EEG screen – normally reached towards the beginning of night. This is when the body heals itself grow tissues, develop bones muscles repair them as well strengthen immune system all these are things that take place at this time.
REM Sleep:
After passing through NREM stages, you will enter REM sleep which is characterized by an increased brain activity similar to being awake. It is a period that is marked by rapid eye movements while being accompanied with higher brain wave patterns and intense dreams which seem real but they are not. This is when all your body muscles are prevented from moving in order to avoid acting out dreams.
What Happens in Your Brain During Sleep?:
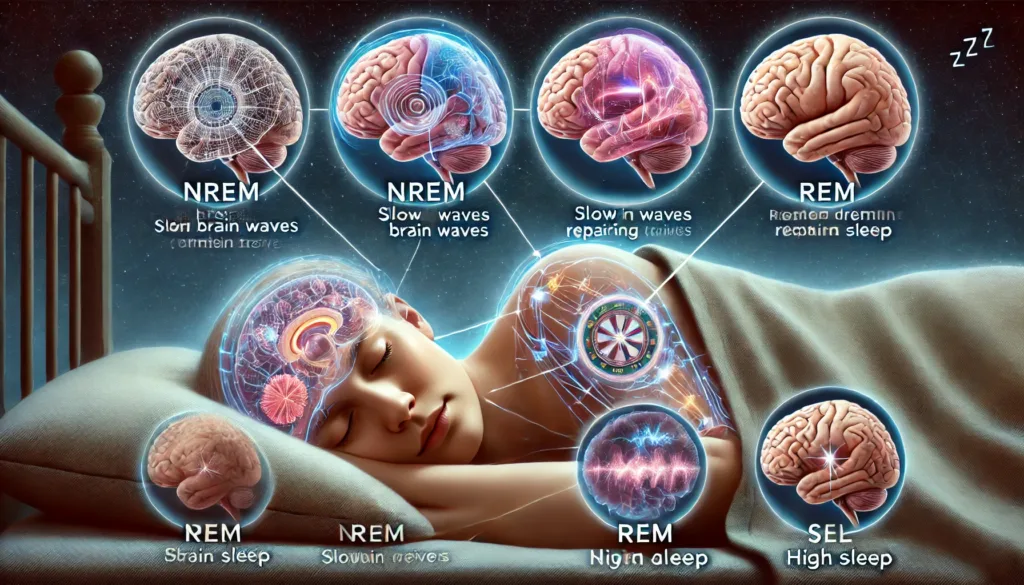
Sleep plays a crucial role in multiple brain functions, like memory consolidation, learning, and emotional regulation. Let’s take a closer look at what happens in your brain health during the various stages of sleep:
Memory Consolidation:
Whilst from morning to night, the human mind acquires information which it may forget or retain. this process involves some stages but mostly takes place in non rapid eye movement(NREM) sleep stages especially deeper ones; also there is sharing between hippocampus region associated with memory where it replays or “reconstructs” the events that occurred earlier that day in order for them to be stored for long periods of time.
Clearing Toxins:
One of the most essential roles of sleep is getting rid of toxins from the brain. Deep sleep makes the brain’s glymphatic system to be more active. This system assists in clearing away all the waste products that have been accumulated during the day that include beta-amyloid which is a protein responsible for Alzheimer’s disease. Sleeping helps keep off these harmful substances hence maintaining the proper functioning of the brain and.

Emotional Regulation:
REM sleep, important as far as concern of emotional regulation is involved, is a stage when an individual’s brain works on their emotions and stores them as memories. It is aimed at enabling an individual handle stress and anxiety more effectively. Failure to have enough REM sleep may result in heightened emotional reactivity hence difficulties in coping with stress.
The Importance of Sleep for Brain Health:
Sleep, sleep, everybody knows how important it is to one’s health, especially to the brain health. Bad sleep can cause cognitive disorders, mood swings and low immunity. Long-term sleeplessness may probably be associated with an increased likelihood of getting Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s.

Tips for Better Sleep:
To make sure your brain gets the rest it requires, note the following advice for improved sleep:
Keep within a sleep schedule: At all times, including weekends, make sure that you go to bed and wake up at the same time.
Have a bedtime routine that is relaxing: Some relaxing activities before sleeping may include reading a book or having warm bath.
Avoid screens: Blue light that is emitted by phones and computers during night time can interrupt your sleep so try lowering your screen time before bedtime.
Develop a comfortable sleep environment: Have a bedroom that is cool, dark and quiet.
Say no to caffeine and heavy meals: Refrain from taking caffeine while closing to sleeping time; Avoid taking heavy meals in order to avoid overweight.
Conclusion:
Let’s not forget about how critical sleep is to the brain health. One way to get insight into the significance of having a sound sleep might be getting to know what happens in our brains during sleep onset.
Make sure that you sleep enough so as to assist this important organ of ours that is involved in cognition and other vital processes thereby promoting better health in general.











1 thought on “Celebrating Brain Health: World Brain Day: How Your Brain Works When You Fall Asleep”